
Understanding Renewable Natural Gas

What is Renewable Natural Gas?
Natural gas, which consists largely of methane, has traditionally been sourced from decomposing organic matter found underground (ie. fossils). However, there are other sources of decomposing organic matter that can generate natural gas. One example is a landfill, which produces gas from its decomposing organic waste. This gas, also known as biogas, can be captured and non-methane elements can be removed, resulting in Renewable Natural Gas (RNG). The resulting RNG is the same as and can be used interchangeably with traditional natural gas; the only difference is that this natural gas came from a landfill instead of a fossil.
Renewable Natural Gas can be produced from a variety of existing waste streams and renewable biomass sources, such as:
- Animal waste from dairies
- Food waste from landfills
- Organic waste from wastewater treatment plants
- Organic waste from landfill-diversion facilities
You can use RNG to power equipment or vehicles that use natural gas, or to generate your own electricity on site. This can be a great way to save money and energy. Other benefits include:
- Capture emissions of unused "waste" methane
- Reduce the need for conventional fuel
- Cut production and waste disposal costs
RNG can be an important renewable energy tool because it is available anytime consumers need it. Wind and solar are intermittent energy sources – meaning the energy isn’t available when the sun isn’t shining, and the wind isn’t blowing. Waste material can be converted into deliverable, renewable energy 24 hours per day, seven days a week and can be deployed when and where it is needed through the pipeline network
Biogas is the raw gas produced from decomposing organic waste. It typically consists of mainly methane and carbon dioxide, along with traces of other elements. In order to become RNG, biogas needs to be cleaned and conditioned, which means removing or reducing non-methane elements such as carbon dioxide. This process generates a Renewable Natural Gas that’s completely interchangeable with traditional pipeline-quality natural gas and ensures safe and reliable operation of the pipeline network and customer equipment. RNG is extremely versatile and can be delivered anywhere along the nation’s extensive pipeline infrastructure.
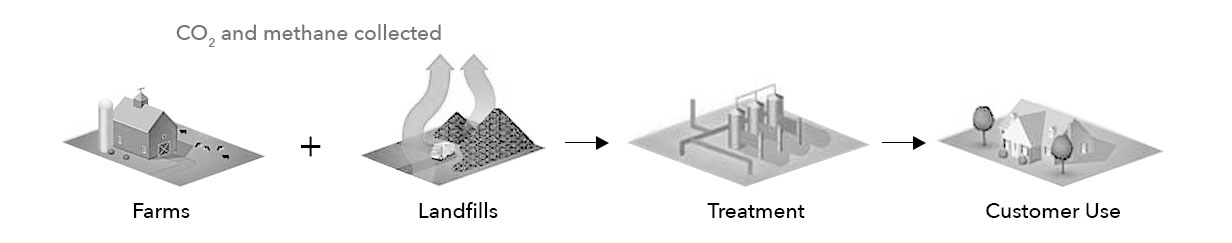
Courtesy of the American Gas Association
The abundance of these materials allows for production of substantial quantities of biogas. A study by UC Davis estimates that more than 20 percent of California’s current residential natural gas use can be provided by RNG derived from our state’s existing organic waste alone2. Looking outside California, the United States could produce up to 10 trillion cubic feet of RNG annually by 2030 — that’s more than five times California’s projected natural gas consumption.
Reducing carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas levels is important to help reduce global warming. RNG is considered a carbon-neutral fuel because it comes from organic sources that once absorbed carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. RNG has even greater benefits when it’s produced from organic waste that would otherwise decay and emit methane emissions into the atmosphere. By capturing more greenhouses gases than it emits, this RNG can be considered carbon-negative!
SoCalGas is a Supporter of Biogas Development and California’s Economy
As part of our commitment to helping the environment and supporting California in meeting its greenhouse gas reduction goals, SoCalGas® offers expertise and assistance to customers who want to convert organic waste material into biogas or RNG. Through our network of natural gas pipelines, SoCalGas offers the opportunity for RNG to be accepted into our transmission and distribution system and delivered to our customers. Converting waste products into RNG can help California meet its energy needs with local resources. Investing in RNG production in California can help create jobs in all regions of the state while improving air quality by better managing our waste streams.