
A fuel cell is a device that runs hydrogen and oxygen through chemical reactions in a process that generates electricity and heat which can be harnessed and captured for use as energy sources. On the outside, a fuel cell often looks like a large basic metallic box; on the inside is a series of “cells” arranged in a stack. Each cell in the stack contains two electrodes: an anode and a cathode, like in a typical battery.
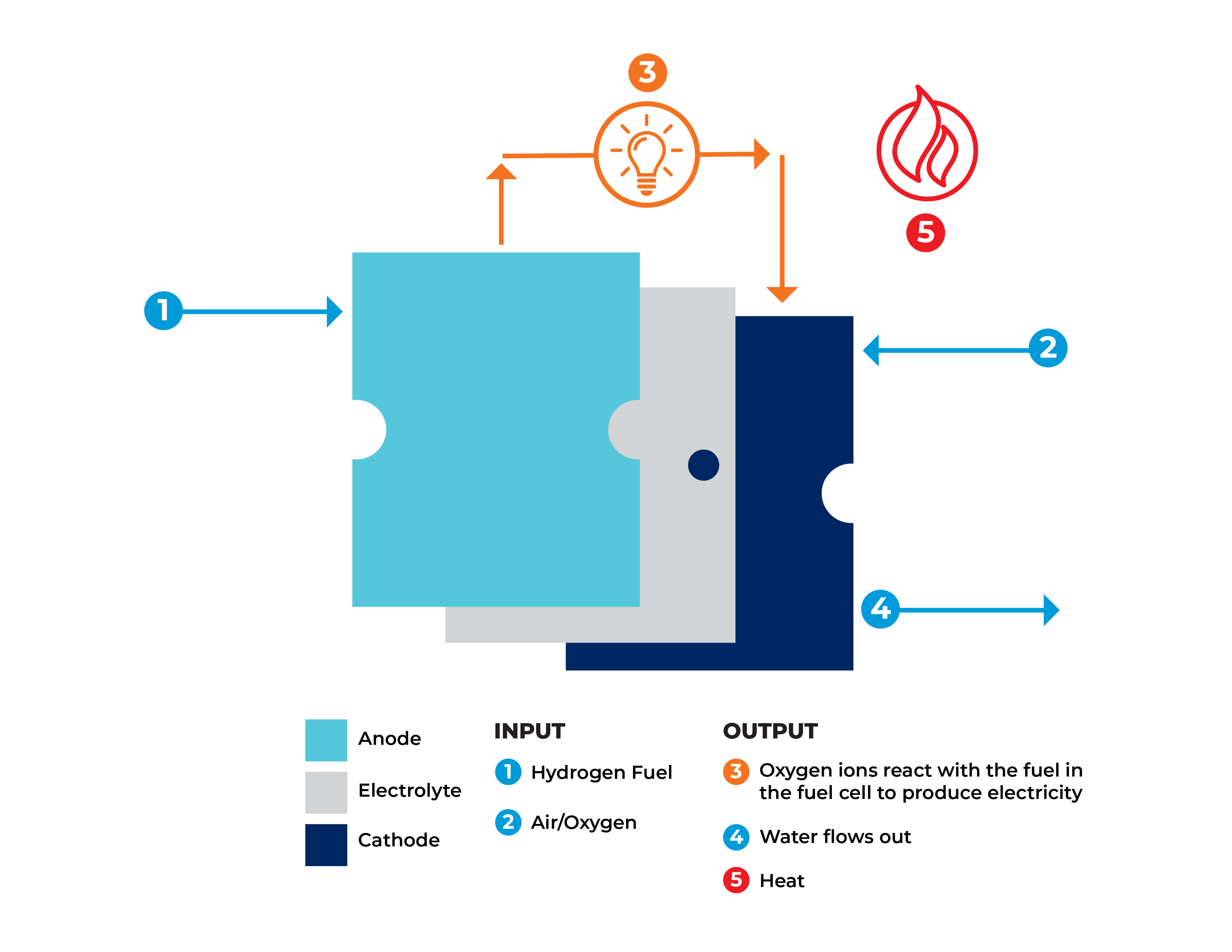
In a fuel cell, hydrogen and oxygen are combined to generate electricity from a fuel source (generally Natural Gas or Hydrogen), with heat, air, and water vapor released as byproducts.
A typical fuel cell works by passing fuel, such as hydrogen, through the anode of a fuel cell and oxygen through the cathode with a catalyst in the middle to separate the fuel molecules into protons and electrons.
- High Efficiency, especially when utilizing co-generation, can attain over 80% energy efficiency
- More environmentally beneficial – low emissions due to a non-combustion process
- More reliable, resilient, and high-quality power produced
Fuel cells can be used in a wide range of applications, including transportation, material handling, stationary, portable, and emergency backup power, base load power, and primary power applications.