Distributed Energy Resource Technologies Overview
Typically, centralized power plants generate electricity and distribute it to end-users through the electric grid. Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) are localized sources of electric generation or storage used to reduce demand or provide supply. DERs systems can usually be sized to meet customers’ particular needs and installed on site. DERs systems may be either connected to the local electric power grid or isolated from the grid in stand-alone applications. DER is a term applied to a wide variety of technologies and consumer products, including fuel cells, microturbines, reciprocating engines, combustion turbines, cogeneration, photovoltaics (PV), and energy storage systems.
24/7 mode: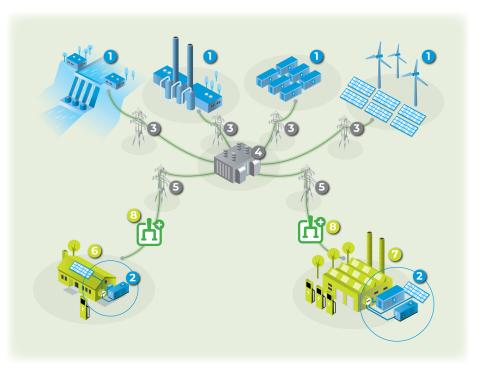
When connected to the electric utility’s lower voltage distributed lines, behind-the-meter microgrids at end-users’ premises can help support the delivery of clean, reliable power to additional customers and reduce electricity losses along transmission and distribution lines. The switch between distribution and end-users is on in this mode. Operating the microgrids in the 24/7 mode can also reduce energy costs for the end-use customers by producing electricity at rates that are less than the electric utilities delivered price and by recovering heat (if applicable) that can be used to displace energy consumption somewhere else at the customer’s premises.
Islanding Mode: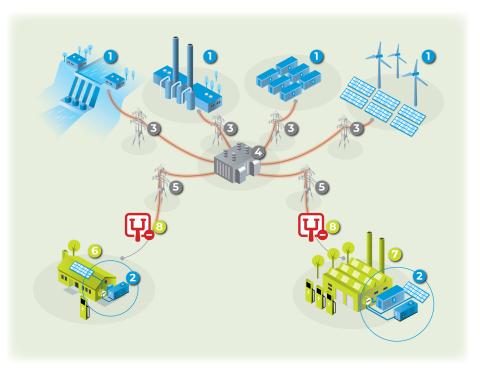
When the electric utility is down or not providing sufficiently stable power, behind-the-meter microgrids can operate in parallel with the grid. The switch between the distribution and end-users is off in the islanding mode. A combination of DER technologies, such as solar, storage, and fuel cells, could provide on-site power generation indefinitely until utility service can be restored. Behind-the-meter microgrids could help increase energy resiliency and power quality.
Supply
1. Power Plants
2. Distributed Generation/Behind-the-meter Microgrids
Delivery
3. Transmission
4. Substation
5. Distribution
Demand
6. Residential End-users
7. Commercial & Industrial (C&I) End-users
8. Switch - Connect or Disconnect to Utility grid
Additional DER Technologies
DER Technologies Include Combined Heat and Power (CHP), Waste Heat to Power, Linear Generator, Power to Gas, Battery Storage, and Solar Photovoltaic.
Benefits of
Distributed Energy Resources
In comparison to paying for power at the rate offered by the electric utilities, customers could reduce their monthly energy bills with the on-site power generation option using DER technologies. Customers can save even more by using the heat associated with the generation of power that is ordinarily wasted, thus avoiding the purchase of the natural gas that would have provided the heat.
Source: CARB Potential Emissions Impact of Public Safety Power Shutoff (PSPS).
Fuel Cell Technologies

Research Development and Demonstration (RD&D)